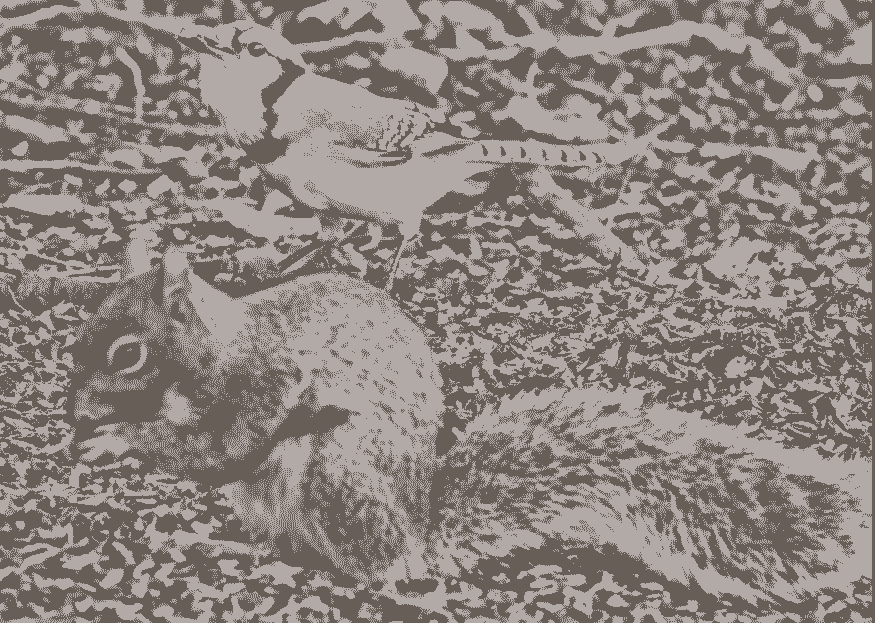
The animal kingdom is full of intricate relationships that often go unnoticed by the human eye. One such fascinating connection exists between blue jays and flying squirrels. While many creatures coexist in harmony, few interactions are as intriguing as the symbiotic relationship between these two species. Understanding how these animals work together not only highlights the wonders of nature but also provides insights into how different species contribute to the health of ecosystems.
In this article, we will explore the nature of the symbiotic relationship between blue jays and flying squirrels, how it benefits both species, and why it’s an essential aspect of their survival.
What is a Symbiotic Relationship?
Before diving into the specifics of the relationship between blue jays and flying squirrels, it’s crucial to understand what a symbiotic relationship is. A symbiotic relationship occurs when two or more species live in close physical proximity and interact in a way that benefits at least one of them. These interactions can be mutualistic (both species benefit), commensal (one benefits without harming the other), or parasitic (one benefits at the expense of the other).
The relationship between blue jays and flying squirrels falls under the category of mutualism, where both species gain benefits from the association. This natural partnership is a perfect example of how animals cooperate in ways that are not always obvious.
What Symbiotic Relationship is Blue Jays and Flying Squirrels?
The relationship between blue jays and flying squirrels is based on a fascinating form of mutual benefit, often revolving around food sources and the safety of their nests. At first glance, these animals may seem unrelated—blue jays are bold, loud birds known for their striking blue feathers, while flying squirrels are small, nocturnal mammals that glide gracefully between trees. Despite their differences, both species rely on similar resources and have developed a way to work together to secure them. ecryptobit.com wallets
Food Sharing and Protection
One of the most prominent aspects of the symbiotic relationship between blue jays and flying squirrels is their food-sharing dynamic. Blue jays are notorious for being opportunistic feeders. They are keen on finding and hoarding nuts, especially acorns. These birds have an exceptional memory and are able to locate and retrieve the acorns they’ve hidden for later consumption.
However, blue jays are not the only ones interested in acorns. Flying squirrels also enjoy these nuts, but unlike blue jays, they prefer to collect them at night, when the birds are less active. Here’s where the mutualistic relationship shines: Blue jays, by collecting acorns and storing them during the day, inadvertently create a food source for the flying squirrels, who often “steal” some of the cached nuts when the jays aren’t around.
In exchange, flying squirrels offer blue jays a form of protection. Flying squirrels are excellent climbers and often build their nests high in the trees. These nests are typically located in hollowed-out trunks or in abandoned woodpecker holes. Blue jays, being loud and territorial birds, often patrol areas where flying squirrels make their homes. This provides a level of protection from other predators, such as owls or hawks, who might otherwise pose a threat to the squirrels.
Seed Dispersal: A Shared Responsibility
Another benefit to both species comes from their role in seed dispersal. Blue jays are well known for their role in spreading acorns, which they often bury to store for the winter. Many of these acorns are forgotten and germinate into oak trees, playing a vital role in the regeneration of forests. Flying squirrels, though primarily nocturnal, feed on various seeds and fruits, including acorns. They may also transport these seeds while moving between trees, further assisting in the dispersal of plant life.
This seed dispersal service benefits both species in the long run. The more trees that grow from dispersed acorns, the more food there is for both blue jays and flying squirrels in future seasons. In this way, both animals play an essential role in the ecosystem, ensuring a continuous food source for generations to come.
Mutual Protection from Predators
Predators are always a concern for small animals, and both blue jays and flying squirrels have developed strategies to protect themselves. For flying squirrels, the biggest threats come from owls, hawks, and other large birds of prey. Blue jays, known for their bold and aggressive nature, are very vocal and have excellent eyesight, which makes them vigilant against approaching predators.
When a threat is detected, blue jays will emit loud calls to warn not only their fellow jays but also the nearby flying squirrels. In return, flying squirrels also use the opportunity to hide or retreat to their nests, where they can remain safely out of sight. This vocal alert system reduces the risk of surprise attacks and gives both species the time they need to escape.
In this mutualistic relationship, the blue jays act as a “sentinel” species, using their vocalizations and heightened alertness to protect their small squirrel companions. In turn, the flying squirrels provide blue jays with an additional layer of protection by occupying high nests, making it harder for predators to target them.
The Role of Blue Jays in the Larger Ecosystem
The blue jay plays a critical role in the forest ecosystem beyond its interactions with flying squirrels. As a highly intelligent and social bird, the blue jay is a key player in maintaining the balance of local ecosystems. Their presence encourages forest regeneration, as they actively contribute to the spread of acorns and other seeds, helping to maintain healthy oak populations.
Furthermore, blue jays are known to be a key part of the food chain. Their diet consists of a wide variety of foods, including insects, fruits, nuts, and seeds, making them an important predator in controlling insect populations. This contributes to a healthier environment for many other species, including flying squirrels.
The Role of Flying Squirrels in Forest Health
Flying squirrels, although small, are incredibly important to the health of forests. Their nocturnal habits help to control insect populations, and they also contribute to the dispersal of seeds from a wide range of plant species, not just acorns. By feeding on a variety of tree seeds, nuts, and fruits, flying squirrels help maintain a diverse and healthy forest ecosystem. Their gliding ability enables them to travel between trees, helping pollinate flowers and spread seeds over vast areas.
Both blue jays and flying squirrels contribute to the biodiversity and resilience of their ecosystems. By sharing resources and helping each other avoid danger, they play a key role in creating a sustainable environment for future generations of wildlife.
Conclusion: Why This Relationship Matters
The symbiotic relationship between blue jays and flying squirrels is a wonderful example of how cooperation can benefit all parties involved. By sharing food resources, protecting one another from predators, and assisting in the dispersal of seeds, both species enhance their chances of survival and contribute to the overall health of their forest ecosystems. Understanding and appreciating this relationship gives us a deeper appreciation for the delicate balance that exists in nature.
Ultimately, the bond between blue jays and flying squirrels reminds us that even in the wild, cooperation is key. These two species work together to create a harmonious and thriving environment, demonstrating the importance of mutualism in the natural world. As we continue to study these relationships, we can gain valuable insights into the interdependence of wildlife and the importance of maintaining biodiversity in our ecosystems.
What symbiotic relationship is blue jays and flying squirrels? It is one of mutual benefit, where both species thrive and help maintain the balance of their environment, ensuring the survival of each other for years to come.